A window is an element that closes a hole in a wall or in a roof. Its tasks include letting sunlight into the room and isolating the interior from outdoor conditions, especially protection from the cold. To determine the thermal insulation properties of the window, a special indicator is used – the heat transfer coefficient.
What is the window heat transfer coefficient?
The window heat transfer coefficient, delineated as Uw,is a parameter indicating how much energy is lost by 1m2 of the partition if the temperature on one side of the partition is lower by 1 K compared to the temperature on the other side of the partition. In other words, this coefficient determines the amount of heat lost when the difference between the temperature of the outside and indoor air is 1 K. This indicator is expressed in W/m2K.

Window heat transfer coefficient – how to calculate it?
A window is a structure consisting of several different types of materials. Therefore, the total heat transfer coefficient is calculated as the result of the heat transfer coefficients of all the elements forming the window. In accordance with PN-EN ISO 10077-1:2017-10,the following relationship shall be used to calculate the resulting heat transfer coefficient of the window:
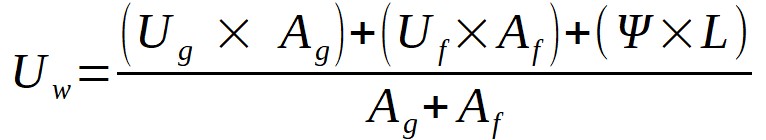
where:
Ug [W/m2K] – heat transfer coefficient of the glass (or other filling). Its value depends on the construction of the glass and the low-carbon technologies used,
A g [m2] – the surface of the visible part of the glass, measured between glazing seals,
U f [W/m2K] – the heat transfer coefficient of the frame, that is, the opaque part of the window. Its value depends primarily on the structure of the frame (its width, number of chambers) as well as the placement of the steel reinforcement in the frame,
A f [m2] – frame area,
? [W/mK] – linear coefficient of heat transfer at the contact of the glass with the frame. It depends mainly on the materials from which the frames between the windows are made (in this regard, aluminum frames work best, and preferably frames fully made of plastic, eg. THERMOBAR?),
L [m] – the length of the glass-frame contact.
Reference Window Dimensions
Based on the above equation, you can see that the Uvalue in depends not only on the quality of the components that make up the window, but also on its dimensions. Due to the need to compare the properties of thermal insulation windows, the concept of a reference window was created. It is a single-leaf window with a width of 1230 mm and a height of 1480 mm. If the windows compared with each other have exactly the same dimensions, their heat transfer coefficients are due only to the different properties of the materials used in the production.

Window heat transfer coefficient and intermeduly frame
The resultantU-factor depends not only on the characteristics of the frame and glass used. It is also affected by the used intermeduly frame. Suppose a window consists of:
- MSline+MD frame with Uf = 0.98 W/m2K,
- U g SUPERtermo glass= 0.5 W/m2K.
By adopting these values, you can calculate the heat transfer coefficients of reference windows with sample frames:
1. Steel intersea frame ? heat frame MS (?=0.055 W/mK) ? Uw = 0.79 W/m2K
2. CHROMATECH Ultra interschoar frame (?=0.028 W/mK) ? Uw = 0.72 W/m2K
3. THERMOBAR intermoving frame (?=0.022 W/mK) ? Uw=0.71 W/m2K


